During a recent customer engagement, the CyberArk Red Team discovered and exploited an Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability (CVE-2024-39708) in Delinea Privilege Manager (formerly Thycotic Privilege Manager). This vulnerability allowed an unprivileged user to execute arbitrary code as SYSTEM. CyberArk responsibly disclosed this vulnerability to Delinea, including the exploit proof of concept (POC) code, as part of our commitment to contributing to the security community.
Analyzing CVE-2024-39708:
Delinea Privilege Manager for Windows, prior to version 12.0.1096, is susceptible to a dynamic-link library (DLL) search order hijacking vulnerability, which allows an unprivileged user to execute arbitrary code as SYSTEM.
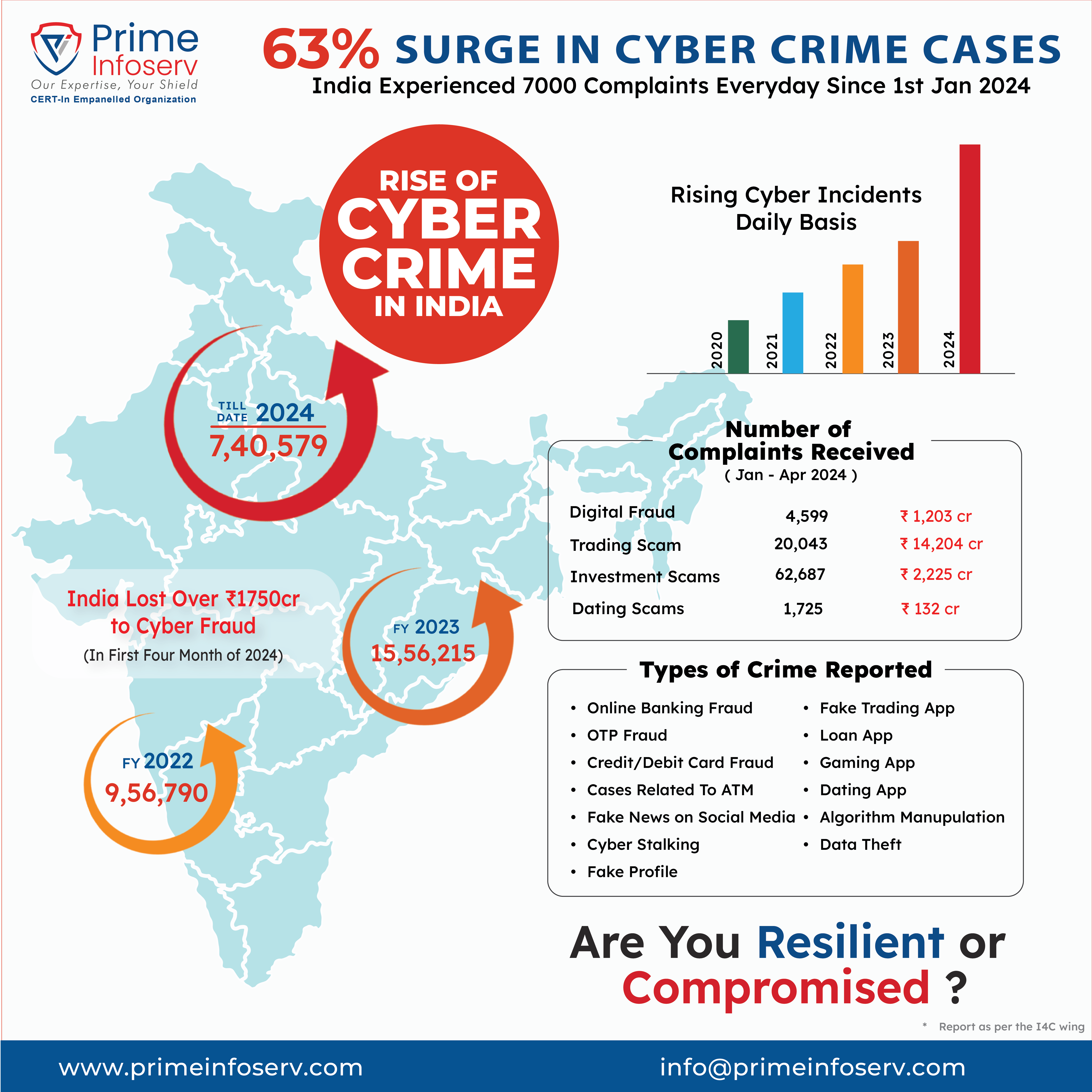
After the agent service starts, it attempts to load httpapi.dll in order from the following paths:
C:\Windows\Temp\Arellia\AmsAgent\Cache\ArelliaAgent\assembly\dl3\7f9cbee9\00bbcf35_70d5d901\
C:\Program Files\Thycotic\Agents\Agent\
C:\Windows\System32\
As shown in Figure 1, the agent service successfully loads httpapi.dll from the System32 directory after failing to locate the DLL in the Windows temp and application installation directories.
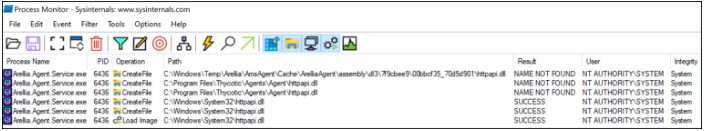
By default, Windows grants unprivileged users permission to write files and folders to C:\Windows\Temp, and unless otherwise specified, this default discretionary access control list (DACL) is inherited by subdirectories. As shown in Figure 2, due to the inherited DACL, the Users group can write files and folders in C:\Windows\Temp\Arellia\AmsAgent\Cache\ArelliaAgent\assembly\dl3\7f9cbee9\00bbcf35_70d5d901.
C:\Windows\Temp\Arellia\AmsAgent\Cache\ArelliaAgent\assembly\dl3\7f9cbee9\00bbcf35_70d5d901
Due to the week DACL, unprivileged users can plant a custom httpapi.dll binary in the directory so that the DLL is found and loaded when the service restarts, resulting in the execution of arbitrary code as SYSTEM.
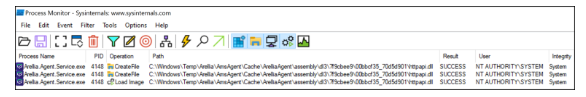
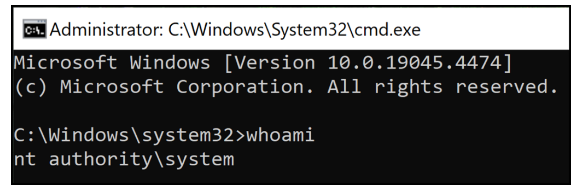
The agent service does not permit unprivileged users to
restart it manually; however, we can force the service to restart and
subsequently load our DLL by rebooting the system or using a clever trick with
some MSI installations. Even if the NoModify setting is configured, which
disables any installation modification via the Apps & Features Windows
settings, the installation repair action can be executed using either the
cached installation package or the installation product code.
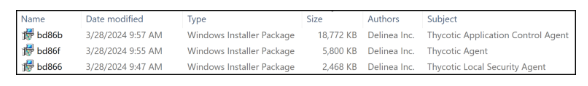
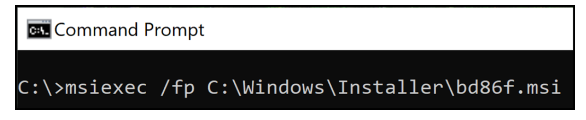
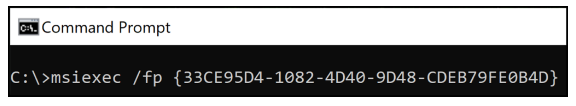
When software is installed using an MSI package, Windows caches the package in the C:\Windows\Installer directory with an alphanumeric file name selected by the Windows Installer. We can execute the repair action on the command line by identifying the cached package for the target installation, for example, by the file Author and Subject attributes
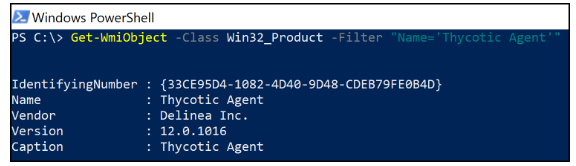
Alternatively, the installation product code can be retrieved from the WMI database or Windows registry, and the repair action can be executed either via the command line or the Application Installation and Servicing Win32 API.
CVE-2024-39708 Disclosure Timeline :
May 29, 2024: CyberArk reported the vulnerability to Delinea and asked for a CVE to be assigned.
May 29, 2024: Delinea acknowledged receiving the disclosure.
June 5, 2024: CyberArk followed up with Delinea, confirming the successful reproduction of the vulnerability using the provided proof of concept (POC).
June 5, 2024: Delinea confirmed that the fix was being tested internally.
June 11, 2024: CyberArk received confirmation from Delinea confirming the assignment of a CVE.
July 1, 2024: Delinea released fixed agent version 12.0.1096.
Discover the advanced strategies CyberArk Red Team Services employs to emulate real-world adversaries and safeguard against vulnerabilities. Learn more about how these tactics can help fortify your defenses by exploring Red Team Services at CyberArk.